-
Mailen Sie uns
yu.li@tiger-transformer.de -
Rufen Sie uns
+49 151 7050 5516
Mailen Sie uns
yu.li@tiger-transformer.deRufen Sie uns
+49 151 7050 5516The sensor as a sensing device plays an absolute role in the control.
Reminiscent of motor controller, it generally contains temperature sensor, currentvoltage sensor, and is directly related to the electric control The motor also has a position sensor, which is what we often call a resolver, or resolver for short.
I remember that I wrote an article about the Hall current sensor before, and today I want to briefly introduce the resolver. I plan to write it in two parts. Other sensors will be briefly introduced later.
Here, my two articles will not involve specific design and control algorithms. To be honest, neither will the author, but from the perspective of structural design, try to figure out the principle .
01.
Introduction to Resolver
The sensor (English name: transducer/sensor) is Can feel the measured information, and can transform the sensed information into electrical signal or other required forms of information output according to certain rules, so as to meet the transmission, processing, storage and display of information Testing devices for requirements such as , recording and control.
Baidu Encyclopedia
First of all, let’s understand the composition diagram of the basic measurement system of sensing and detection technology:
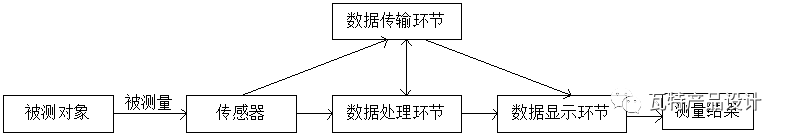
Secondly, look at the composition diagram of the sensor:

Classified according to the detection amount of the sensor:
< img src="/static/upload/image/20230605/10473521.jpg" alt="image" />
The resolver is a kind of displacement sensor, but it measures the angle, its advantages and disadvantages As follows:
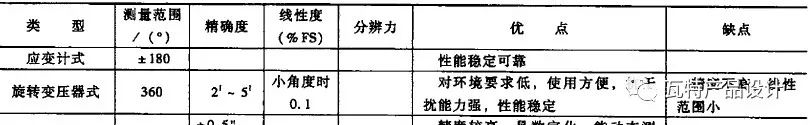
Also follow to work In terms of principle, the resolver is a magnetoelectric induction type, also known as a magnetoelectric sensor.
Basic principle:
Using the electromagnetic induction principle will be measured ( Such as vibration, displacement, speed, etc.) into a sensor that converts electrical signals. It is an active sensor that can convert the mechanical quantity of the measured object into an easy-to-measure electrical signal without an auxiliary power supply. Because of its high output power, stable performance and certain working bandwidth (10-1000 Hz), it is widely used.
Speaking of electromagnetic induction, let’s talk about Electricity-->Magnetism first;
Everyone should have learned Ampere for high school physics knowledge Rule:
Ampere's rule, also known as the right-hand spiral rule, is a rule that expresses the relationship between the direction of the current and the direction of the magnetic field of the magnetic field excited by the current. Ampere's law in the current-carrying straight wire (Ampere's law 1): hold the current-carrying straight wire with the right hand, let the thumb point to the direction of the current in the straight wire, then the four fingers point to the direction of the magnetic field around the current-carrying wire; in the current-carrying solenoid Ampere's law (Ampere's law 2): Hold the energized solenoid with your right hand, and let the four fingers point to the direction of the current, then the end pointed by the thumb is the N pole of the energized solenoid.
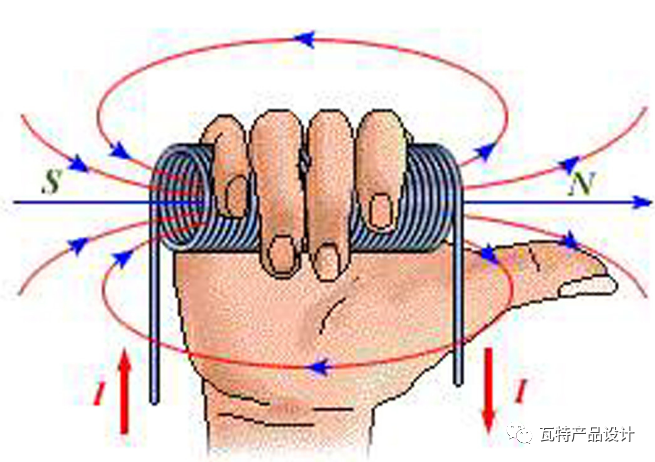
If there is current in the spiral tube, a magnetic field will be generated .
Next, let’s talk about magnetism-->electricity;
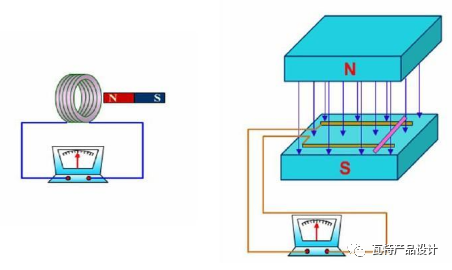
It is also knowledge in high school, Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction:
Electromagnetic induction The law is also called Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction refers to the phenomenon of induced electromotive force due to the change of magnetic flux. For example, when a part of the conductor of the closed circuit moves to cut the magnetic induction line in the magnetic field, the conductor will generate current. The current is called induced current, and the generated electromotive force (voltage) is called induced electromotive force.
The change of magnetic flux will generate induced electromotive force.
Last words
Today, we briefly explain the sensors and their different classifications.
Know that the resolver belongs to the magnetic induction sensor **** according to the working principle.
Currently, only the principles behind the generation of magnetism and electricity by magnetism are explained, so how does the specific resolver use these principles to detect the angle between the rotor and the stator of the motor Woolen cloth?